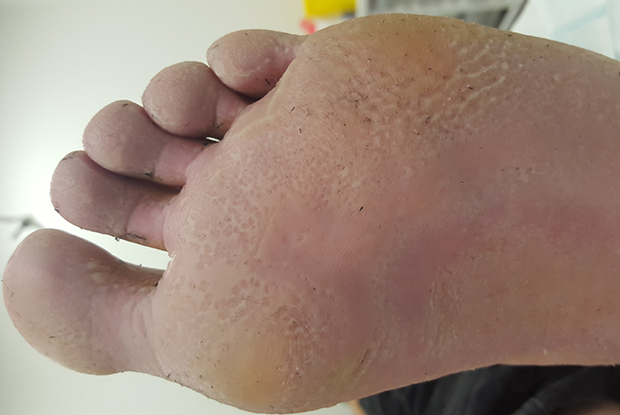
What is Pitted Keratolysis?
Pitted Keratolysis is a superficial bacterial infection of the skin. The name is derived from skin (Kerato) and its break down (lysis). This condition affects the soles of the feet and sometimes the palms of the hands. It is also one of the many causes of smelly feet.
What causes Pitted Keratolysis?
This condition is caused by several bacterial species, including corynebacteria, Dermatophilus congolensis, Kytococcus sedentarius, actinomyces and streptomyces. The bacteria proliferate in moist conditions. The pitting is due to destruction of the horny cells (stratum corneum) by protease enzymes produced by the bacteria. The bad smell is due to sulphur compounds produced by the bacteria: thiols, sulphides and thioesters.
Several other factors can also cause pitted keratolysis, such as hot humid weather, occlusive footwear i.e. rubber boots or vinyl shoes, thickened skins of palms and soles (keratoderma), and excessive swearing of hands and feet (hyperhidrosis).
Signs and symptoms of Pitted Keratolysis
- Mostly affects the soles, forefoot, the heel or both. Palms are rarely infected.
- Results in a whitish skin surface with clusters of multiple, fine punched-out pits.
- Pits often join together (coalesce) to form larger, crater-like lesion.
- A variant of pitted keratolysis presents with diffuse red areas on the soles.
Who is most at risk of developing Pitted Keratolysis?
Pitted keratolysis is much more common in males than in females. Occupations at risk include:
- Farmers
- Athletes
- Sailors or fishermen
- Industrial workers
- Military personnel
Females offering pedicure and foot care in a spa salon may also be affected by pitted keratolysis.
Diagnosis and treatment
Pitted keratolysis is usually diagnosed clinically. Swabs are rarely required. However, the causative organisms may be identified from the pitted lesions and cultured on brain heart infusion agar. Skin scrapings are often taken to exclude fungal infection. Wood light examination displays a characteristic coral red fluorescence in some cases. The diagnosis is sometimes made by skin biopsy revealing characteristic histopathological features of pitted keratolysis.
Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotic and antiseptic therapy. Before commencing any treatment it is essential that you see a doctor first.
What can I do to prevent getting pitted Keratolysis?
Pitted keratolysis will quickly recur unless the feet are kept dry. The following precautions should be taken to prevent recurrences:
- Wear boots for as short a period as possible
- Wear socks which effectively absorb sweat, i.e. cotton and/or wool
- Wear open-toed sandals whenever possible
- Wash feet with soap or antiseptic cleanser twice daily
- Apply antiperspirant to the feet at least twice weekly
- Do not wear the same shoes two days in a row — dry them out
- Do not share footwear or towels with others.
If you are concerned that you may have pitted keratolysis feel free to visit us at our Marrickville clinic and one of our experienced podiatrists can assist you. We will take you a thorough history and conduct a detailed assessment to ensure the correct diagnosis.
Stay warm and have a great day!
Share this post:
Recent Posts

Hip Dysplasia: A Guide for Parents and Adults
Hip dysplasia (developmental dysplasia of the hip – DDH) is a condition that affects the hip joint.

Heel Spurs: Understanding the Cause and Finding Relief
Heel pain can be a real drag, especially when that first step in the morning feels like stepping on a tack. One culprit behind this discomfort can be heel spurs. But what exactly are they, and more importantly, how can you fix them?
Conquering Foot Pain: Effective Strategies for Arthritic Feet
Arthritis in the feet can significantly disrupt your daily life, turning simple walks into painful struggles.
Blisters Be Gone: How to Keep Your Feet Happy on Every Run
Blisters – the bane of a runner’s existence. Those pesky little pockets of fluid can turn a joyful run into a painful slog. But fear not, fellow runner!


